- when a piece of code should be called (call stack)
- within some context (piece of heap)
1 - Context concepts
Scope
Scope is the accessibility of variables, functions, and objects in some particular part of your code during runtime.
Global Scope vs Local Scope
Global scope lives as long as your application lives. Local Scope lives as long as your functions are called and executed.
Block Statements : "var" vs "let" "const"
Contrary to the var keyword, the let and const keywords support the declaration of local scope inside block statements.
Context vs Execution Context
Context is used to refer to the value of "this" in some particular part of your code. Each function creates its own execution context (related to Scope).
Lexical Scope vs Closure
A closure is the combination of a function bundled together (enclosed) with references to its surrounding state (the lexical environment); Lexical Scope means that in this nested group of functions, the inner functions have access to the variables and other resources of their parent scope.
ES5 Function vs ES6 Arrow function
Much more than a "syntactic sugar" but a real useful tool coming with ES6.
Conclusion
In brief, when it's possible: let, const, arrow function
No more reason to bypass now:
Resources
- Scope summary: https://scotch.io/tutorials/understanding-scope-in-javascript
- Fat arrow: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/when-and-why-you-should-use-es6-arrow-functions-and-when-you-shouldnt-3d851d7f0b26/
- JS equality: https://dorey.github.io/JavaScript-Equality-Table/
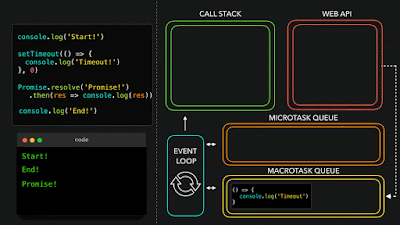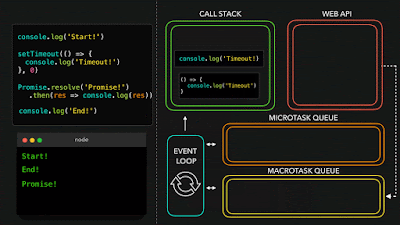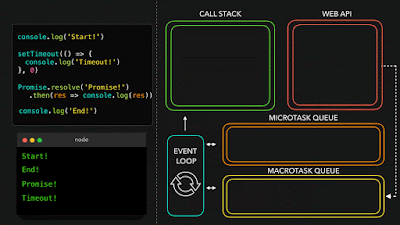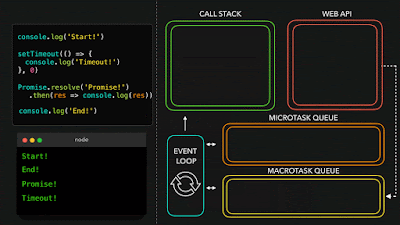
2 - Async
JavaScript has a concurrency model based on an event loop, which is responsible for executing the code, collecting and processing events, and executing queued sub-tasks.
Callbacks vs Promises... vs Async
But also generators, observables and other reactive way of writing asynchronous code...
In brief, when it's possible: async , await
No more reason to bypass now:
Resources
... Final challenge solution
One solution can be found here : https://plnkr.co/edit/JTDgFGu1LaIq7HEO?preview
Hope it helps you to write better Javascript code ?!